We have tested a variety of Large Language Models (LLMs) tools and services and selected the best ones for you.
Here we are listing the top 15 Large Language Models (LLMs) tools that we recommend.
Theee.ai: Access Over 50,000 GPTs Tools Powered by GPT4o for Free
LLM-X
Franz Extractor & Classifier
AI Checker
AI Tools 99
Protip
SaaSrefs
iNCSAI List
Every AI Image
fireworks.ai
UncensorGPT
GptHub.best
The Octagon Oracle: Next Generation UFC Fight Picks Powered By AI
GPT App Store
Magic Docs
Large Language Models (LLMs) Use Cases
Large Language Models (LLMs) Use Cases
- #1
1. Content generation: Large language models can be used to automatically generate high-quality content for websites, blogs, and social media posts. This can save time and resources for businesses looking to consistently produce fresh and engaging content.
- #2
2. SEO optimization: LLMs can help SEO copywriters optimize website content by suggesting relevant keywords, improving readability scores, and generating meta descriptions. This can lead to higher search engine rankings and increased organic traffic.
- #3
3. Personalized recommendations: By analyzing user behavior and preferences, large language models can provide personalized product recommendations, content suggestions, and email marketing messages. This can improve the user experience and drive higher conversion rates.
- #4
4. Sentiment analysis: LLMs can be used to analyze customer feedback, reviews, and social media comments to gauge public sentiment towards a brand or product. This information can help businesses make data-driven decisions and launch targeted marketing campaigns.
- #5
5. Multilingual content creation: Large language models have the ability to generate content in multiple languages, allowing businesses to reach a global audience with localized and culturally relevant messaging. This can help expand brand awareness and drive international growth.
What are the key features and capabilities of large language models (LLMs)?
What are the key features and capabilities of large language models (LLMs)?
Large language models (LLMs) are a type of artificial intelligence (AI) that are trained on vast amounts of text data to develop a deep understanding of natural language. Key features of LLMs include their ability to generate human-like text, engage in open-ended dialogue, answer questions, and even complete complex tasks such as summarization, translation, and code generation. LLMs leverage deep learning techniques, particularly transformers, to capture contextual relationships within language and develop sophisticated language understanding.
These models excel at tasks that require general intelligence and language comprehension, making them valuable tools for a wide range of applications, from chatbots and virtual assistants to content generation and text analysis. The scale and complexity of LLMs have enabled breakthroughs in areas like natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML), pushing the boundaries of what is possible with AI-powered language understanding and generation.
How are LLMs trained and what are the key technical considerations in their development?
How are LLMs trained and what are the key technical considerations in their development?
Large language models are typically trained using large unsupervised datasets of text, such as books, articles, and web pages. The training process involves self-supervised learning, where the model learns to predict the next word in a sequence of text, gradually building a comprehensive understanding of language structure and semantics.
The technical considerations in developing LLMs include:
- Model architecture: The choice of neural network architecture, such as transformers, which enable efficient processing of long-range dependencies in language.
- Dataset curation: The selection and preprocessing of large, diverse, and high-quality text datasets to ensure the model learns from a broad and representative set of language.
- Computational resources: The immense computational power and storage required to train these models, often requiring specialized hardware like GPUs and TPUs.
- Model scaling: Techniques to scale up the size and complexity of LLMs, often resulting in improved performance but increased model complexity and training costs.
- Optimization and fine-tuning: Strategies to optimize the model's training process and fine-tune it for specific tasks or applications.
The continuous advancements in these technical areas have enabled the development of increasingly capable and versatile large language models.
What are the key application areas and use cases for large language models?
What are the key application areas and use cases for large language models?
Large language models have a wide range of applications and use cases, including:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): LLMs excel at tasks like text generation, question answering, sentiment analysis, machine translation, and text summarization.
- Conversational AI: LLMs power chatbots, virtual assistants, and dialogue systems, enabling more natural and engaging interactions.
- Content Creation: LLMs can assist in article writing, storytelling, creative writing, and the generation of various types of text-based content.
- Code Generation: LLMs can be used to generate and refine code, making them valuable tools for software development and programming tasks.
- Knowledge Extraction: LLMs can be used to extract insights and information from large text corpora, supporting research, analysis, and decision-making.
- Multimodal Applications: LLMs can be combined with computer vision and other AI modalities to enable multimodal interactions and cross-modal understanding.
The versatility and continuous advancements in LLM capabilities are driving their adoption across a wide range of industries and applications, transforming how we interact with and leverage AI-powered language technology.
What are the key ethical considerations and challenges associated with the development and deployment of large language models?
What are the key ethical considerations and challenges associated with the development and deployment of large language models?
The widespread adoption and increasing capabilities of large language models have raised several ethical considerations and challenges, including:
- Bias and Fairness: LLMs can perpetuate and amplify societal biases present in their training data, leading to biased outputs and potentially discriminatory applications.
- Privacy and Data Rights: The vast datasets used to train LLMs raise concerns about data privacy, consent, and the rights of individuals whose information is included in the training data.
- Transparency and Explainability: The complexity of LLMs can make it challenging to understand their inner workings and decision-making processes, reducing transparency and accountability.
- Misuse and Malicious Applications: LLMs can be misused for generating disinformation, impersonation, and other malicious purposes, posing risks to individual and societal well-being.
- Environmental Impact: The energy-intensive training and deployment of LLMs can have a significant environmental impact, raising sustainability concerns.
- Job Displacement: The automation of certain tasks through LLM-powered applications may lead to job displacement and changes in the labor market.
Addressing these ethical considerations requires a collaborative effort involving researchers, developers, policymakers, and the public to ensure the responsible and beneficial development and deployment of large language models.
How do large language models compare to other AI approaches, and what are the potential future developments and trends in this field?
How do large language models compare to other AI approaches, and what are the potential future developments and trends in this field?
Large language models represent a significant advancement in artificial intelligence and natural language processing, but they differ from and complement other AI approaches in several ways:
- Narrow vs. General AI: LLMs are examples of general AI systems that can adapt to a wide range of language-related tasks, in contrast to narrow AI systems that are specialized for specific applications.
- Data-driven vs. Rule-based: LLMs rely on data-driven, machine learning-based approaches, whereas traditional rule-based NLP systems are based on handcrafted linguistic rules.
- Contextual Understanding: LLMs excel at capturing contextual relationships and understanding language in context, a limitation of earlier rule-based NLP approaches.
Looking to the future, potential developments and trends in the large language model field include:
- Increased Model Size and Complexity: Continued scaling of LLMs to unlock even more advanced language understanding and generation capabilities.
- Multimodal Integration: Combining LLMs with computer vision, speech recognition, and other AI modalities to enable more holistic and interactive experiences.
- Specialization and Domain Adaptation: Techniques to fine-tune and adapt LLMs for specific applications and industries, leveraging their general capabilities.
- Improved Interpretability and Explainability: Developing methods to make the inner workings of LLMs more transparent and understandable.
- Safer and More Ethical AI: Advancements in bias mitigation, privacy preservation, and responsible development of LLMs.
As the field of large language models continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more transformative applications and impacts on how we interact with and leverage AI-powered language technology.
- Theee.ai: Access Over 50,000 GPTs Tools Powered by GPT4o for Free
- Theee.ai: Access Over 50,000 GPTs Tools Powered by GPT4o for Free
- LLM-X
- LLM-X
- Franz Extractor & Classifier
- Franz Extractor & Classifier
- AI Checker
- AI Checker
- AI Tools 99
- AI Tools 99
- SaaSrefs
- SaaSrefs
- iNCSAI List
- iNCSAI List
- Every AI Image
- Every AI Image
- fireworks.ai
- fireworks.ai
- UncensorGPT
- UncensorGPT
- GptHub.best
- GptHub.best
- The Octagon Oracle: Next Generation UFC Fight Picks Powered By AI
- The Octagon Oracle: Next Generation UFC Fight Picks Powered By AI
- GPT App Store
- GPT App Store
- Magic Docs
- Magic Docs
Example of Large Language Models (LLMs) Tools
Example of Large Language Models (LLMs) Tools
Open Interpreter

Open Interpreter is a project that allows large language models (LLMs) to run code on your computer, enabling them to complete a wide range of tasks.
Store for GPTs

Store for GPTs is a platform that allows users to browse, access, and utilize various large language models (GPTs) for their applications and projects. It provides a centralized hub where users can discover, compare, and integrate different GPT models into their workflows.
LLM-X
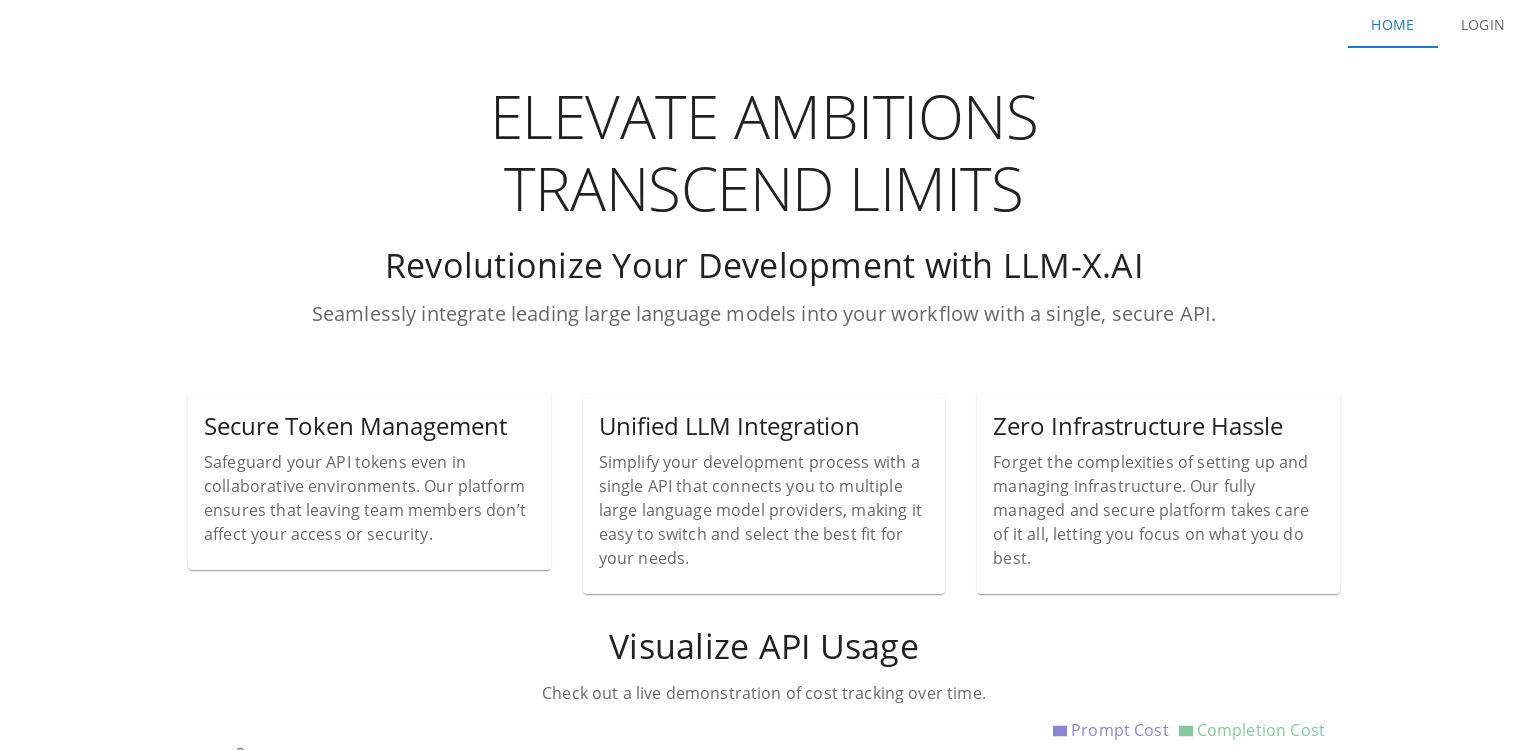
LLM-X is a SAAS platform that enables seamless integration of leading large language models into your workflow through a single, secure API. It simplifies the development process by providing unified access to multiple language models, allowing you to easily switch and select the best fit for your needs. The platform also offers secure token management, zero infrastructure hassle, and cost tracking features, empowering you to focus on your core development tasks without the complexities of managing the underlying infrastructure.
Conclusion
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Large Language Models (LLMs) tools listed above are the best in their class. They offer a wide range of features and functionalities that cater to different needs and preferences. Whether you're looking for a tool to streamline your workflow, enhance your productivity, or drive innovation, these tools have got you covered. We recommend exploring each tool further, taking advantage of free trials or demos, and gathering feedback from your team to make an informed decision. By leveraging the capabilities of these cutting-edge tools, you can unlock new opportunities, drive growth, and stay ahead in today's competitive landscape.
Similar Categories
Similar Categories